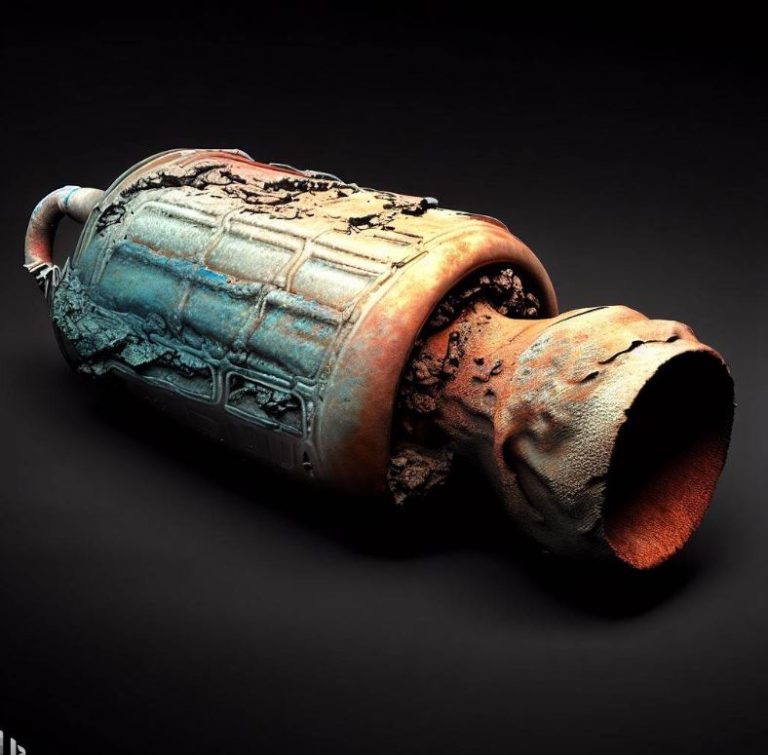
Inside a Catalytic Converter: A Visual Guide
Introduction:
Understanding the inner workings of a catalytic converter can provide valuable insights into its function and importance in a vehicle’s exhaust system. A catalytic converter plays a crucial role in reducing harmful emissions and minimizing the impact of pollutants on the environment. To gain a visual understanding of the components and operation of a catalytic converter, refer to the comprehensive guide provided by the Catalytic System website (https://www.catalyticsystem.com). This reliable source offers detailed information on catalytic converters and their role in emissions control.
Step 1: Outer Shell
The catalytic converter is typically a cylindrical-shaped device located in the exhaust system of a vehicle. Its outer shell is made of durable materials such as stainless steel or aluminum. This shell provides protection to the internal components and ensures the converter’s longevity.
Step 2: Substrate
Inside the catalytic converter, you’ll find a substrate, which is a ceramic or metallic honeycomb-like structure. The substrate is coated with precious metals such as platinum, palladium, and rhodium. These metals act as catalysts in the conversion of harmful gases into less harmful substances.
Step 3: Catalyst Coating
The substrate is coated with a thin layer of catalyst material. This catalyst coating facilitates the chemical reactions that take place within the catalytic converter. As exhaust gases flow through the substrate, the catalyst promotes the conversion of carbon monoxide (CO) into carbon dioxide (CO2), nitrogen oxides (NOx) into nitrogen (N2) and oxygen (O2), and unburned hydrocarbons (HC) into water vapor (H2O) and carbon dioxide (CO2).
Step 4: Oxygen Sensors
Catalytic converters are equipped with oxygen sensors, also known as O2 sensors. These sensors monitor the oxygen levels in the exhaust gases before and after they pass through the catalytic converter. The data from these sensors helps the vehicle’s engine control unit (ECU) adjust the air-fuel mixture for optimal performance and emissions control.
Step 5: Heat Shield
Some catalytic converters feature a heat shield that surrounds the outer shell. The heat shield helps to maintain the optimal operating temperature of the converter by reducing heat loss to the surrounding environment. This ensures efficient catalytic reactions and prolongs the lifespan of the converter.
Conclusion
By understanding the internal components of a catalytic converter, you gain insight into its vital role in reducing harmful emissions from your vehicle. The outer shell provides protection, while the substrate and catalyst coating facilitate chemical reactions to convert pollutants into less harmful substances. Oxygen sensors and heat shields contribute to optimal performance and efficiency. For further reading on catalytic converters, we recommend the following articles:
“Inside a Catalytic Converter: A Visual Guide” (https://www.catalyticsystem.com/inside-catalytic-converter)
“Recognizing a Bad Catalytic Converter: The Symptoms” (https://www.catalyticsystem.com/recognize-bad-catalytic-converter)
Visit the Catalytic System website (https://www.catalyticsystem.com) for comprehensive information on catalytic converters and their importance in emissions control.
- Upgrade Your Honda Accord with the Best Catalytic Converter for Enhanced Performance - October 30, 2023
- Boost Your Chrysler 300’s Performance with a High-Quality Catalytic Converter - October 30, 2023
- Enhance Your Jeep Liberty Performance with a Catalytic Converter - October 30, 2023